Bitcoin v0.1 released
2009 Jan 8
See all posts
Bitcoin v0.1 released @ Satoshi Nakamoto
- Author
-
Satoshi Nakamoto
- Email
-
satoshinakamotonetwork@proton.me
- Site
-
https://satoshinakamoto.network
I have put the Bitcoin v0.1 release announcement on the Cryptography
mailing list.
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system
that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It's
completely decentralized with no server or central authority.
Here are 3 screenshots of the client's UI.
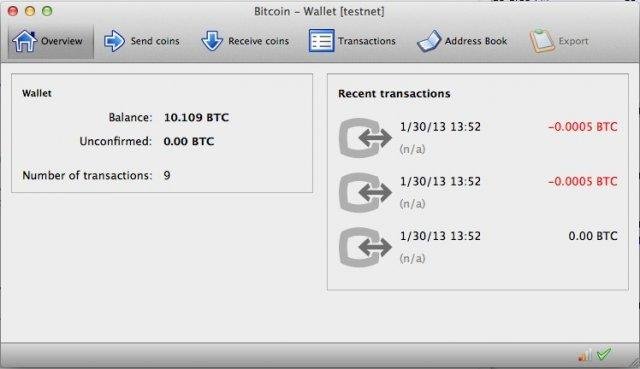
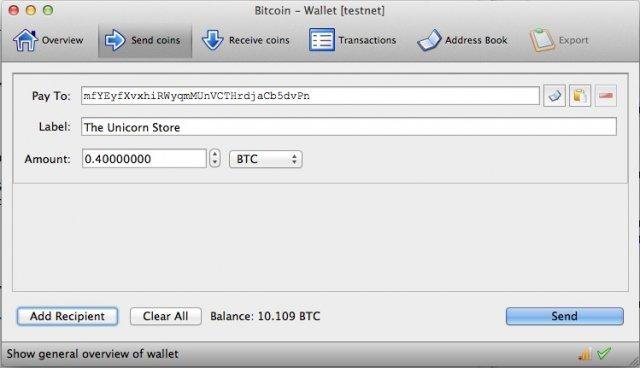
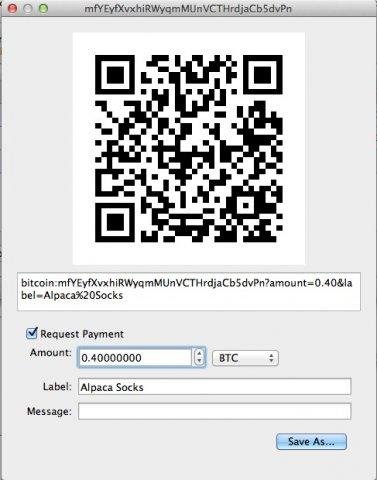
Download link:
http://downloads.sourceforge.net/bitcoin/bitcoin-0.1.0.rar
Windows only for now. Open source C++ code is included.
- Unpack the files into a directory
- Run BITCOIN.EXE
- It automatically connects to other nodes
If you can keep a node running that accepts incoming connections,
you'll really be helping the network a lot. Port 8333 on your firewall
needs to be open to receive incoming connections.
The software is still alpha and experimental. There's no guarantee
the system's state won't have to be restarted at some point if it
becomes necessary, although I've done everything I can to build in
extensibility and versioning.
You can get coins by getting someone to send you some, or turn on
Options->Generate Coins to run a node and generate blocks. I made the
proof-of-work difficulty ridiculously easy to start with, so for a
little while in the beginning a typical PC will be able to generate
coins in just a few hours. It'll get a lot harder when competition makes
the automatic adjustment drive up the difficulty. Generated coins must
wait 120 blocks to mature before they can be spent.
There are two ways to send money. If the recipient is online, you can
enter their IP address and it will connect, get a new public key and
send the transaction with comments. If the recipient is not online, it
is possible to send to their Bitcoin address, which is a hash of their
public key that they give you. They'll receive the transaction the next
time they connect and get the block it's in. This method has the
disadvantage that no comment information is sent, and a bit of privacy
may be lost if the address is used multiple times, but it is a useful
alternative if both users can't be online at the same time or the
recipient can't receive incoming connections.
Total circulation will be 21,000,000 coins. It'll be distributed to
network nodes when they make blocks, with the amount cut in half every 4
years.
first 4 years: 10,500,000 coins
next 4 years: 5,250,000 coins
next 4 years: 2,625,000 coins
next 4 years: 1,312,500 coins
etc...
When that runs out, the system can support transaction fees if
needed. It's based on open market competition, and there will probably
always be nodes willing to process transactions for free.
Satoshi Nakamoto
Bitcoin
v0.1 release on P2P Foundation forum on Feb 11, 2009
I've developed a new open source P2P e-cash system called Bitcoin.
It's completely decentralized, with no central server or trusted
parties, because everything is based on crypto proof instead of trust.
Give it a try, or take a look at the screenshots and design paper:
Download Bitcoin v0.1 at https://www.bitcoin.org
The root problem with conventional currency is all the trust that's
required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase
the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of
that trust. Banks must be trusted to hold our money and transfer it
electronically, but they lend it out in waves of credit bubbles with
barely a fraction in reserve. We have to trust them with our privacy,
trust them not to let identity thieves drain our accounts. Their massive
overhead costs make micropayments impossible.
A generation ago, multi-user time-sharing computer systems had a
similar problem. Before strong encryption, users had to rely on password
protection to secure their files, placing trust in the system
administrator to keep their information private. Privacy could always be
overridden by the admin based on his judgment call weighing the
principle of privacy against other concerns, or at the behest of his
superiors. Then strong encryption became available to the masses, and
trust was no longer required. Data could be secured in a way that was
physically impossible for others to access, no matter for what reason,
no matter how good the excuse, no matter what.
It's time we had the same thing for money. With e-currency based on
cryptographic proof, without the need to trust a third party middleman,
money can be secure and transactions effortless.
One of the fundamental building blocks for such a system is digital
signatures. A digital coin contains the public key of its owner. To
transfer it, the owner signs the coin together with the public key of
the next owner. Anyone can check the signatures to verify the chain of
ownership. It works well to secure ownership, but leaves one big problem
unsolved: double-spending. Any owner could try to re-spend an already
spent coin by signing it again to another owner. The usual solution is
for a trusted company with a central database to check for
double-spending, but that just gets back to the trust model. In its
central position, the company can override the users, and the fees
needed to support the company make micropayments impractical.
Bitcoin's solution is to use a peer-to-peer network to check for
double-spending. In a nutshell, the network works like a distributed
timestamp server, stamping the first transaction to spend a coin. It
takes advantage of the nature of information being easy to spread but
hard to stifle. For details on how it works, see the design paper at Bitcoin:
A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
The result is a distributed system with no single point of failure.
Users hold the crypto keys to their own money and transact directly with
each other, with the help of the P2P network to check for
double-spending.
Satoshi Nakamoto
https://www.bitcoin.org
Here are 3 screenshots of the client's UI.



BitCoin v0.01 ALPHA
Copyright (c) 2009 Satoshi Nakamoto Distributed under the MIT/X11
software license, see the accompanying file license.txt or
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php. This product
includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the
OpenSSL Toolkit (http://www.openssl.org/). This product includes
cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
Intro
Bitcoin is an electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network
to prevent double-spending. It's completely decentralized with no server
or central authority.
Operating Systems
Windows NT/2000/XP (and probably Vista)
Vista hasn't been tested yet. All the libraries used are
cross-platform, so there's nothing preventing future Linux and Mac
builds.
Setup
Unpack the files into a directory and run bitcoin.exe.
The software automatically finds other nodes to connect to. You
should set your firewall to forward port 8333 to your computer so you
can receive incoming connections, otherwise the nodes you can connect
with will be limited.
To support the network by running a node, select:
Options->Generate Coins
and keep the program open or minimized. It runs at idle priority when
no other programs are using the CPU. Your computer will be solving a
very difficult computational problem that is used to lock in blocks of
transactions. The time to generate a block varies each time, but may
take days or months, depending on the speed of your computer and the
competition on the network. It's not a computation that has to start
over from the beginning if you stop and restart it. A solution might be
found at any given moment it's running. As a reward for supporting the
network, you receive coins when you successfully generate a block.
Bitcoin v0.1 released
2009 Jan 8 See all postsSatoshi Nakamoto
satoshinakamotonetwork@proton.me
https://satoshinakamoto.network
I have put the Bitcoin v0.1 release announcement on the Cryptography mailing list.
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It's completely decentralized with no server or central authority.
Here are 3 screenshots of the client's UI.
Download link:
http://downloads.sourceforge.net/bitcoin/bitcoin-0.1.0.rar
Windows only for now. Open source C++ code is included.
If you can keep a node running that accepts incoming connections, you'll really be helping the network a lot. Port 8333 on your firewall needs to be open to receive incoming connections.
The software is still alpha and experimental. There's no guarantee the system's state won't have to be restarted at some point if it becomes necessary, although I've done everything I can to build in extensibility and versioning.
You can get coins by getting someone to send you some, or turn on Options->Generate Coins to run a node and generate blocks. I made the proof-of-work difficulty ridiculously easy to start with, so for a little while in the beginning a typical PC will be able to generate coins in just a few hours. It'll get a lot harder when competition makes the automatic adjustment drive up the difficulty. Generated coins must wait 120 blocks to mature before they can be spent.
There are two ways to send money. If the recipient is online, you can enter their IP address and it will connect, get a new public key and send the transaction with comments. If the recipient is not online, it is possible to send to their Bitcoin address, which is a hash of their public key that they give you. They'll receive the transaction the next time they connect and get the block it's in. This method has the disadvantage that no comment information is sent, and a bit of privacy may be lost if the address is used multiple times, but it is a useful alternative if both users can't be online at the same time or the recipient can't receive incoming connections.
Total circulation will be 21,000,000 coins. It'll be distributed to network nodes when they make blocks, with the amount cut in half every 4 years.
first 4 years: 10,500,000 coins
next 4 years: 5,250,000 coins
next 4 years: 2,625,000 coins
next 4 years: 1,312,500 coins
etc...
When that runs out, the system can support transaction fees if needed. It's based on open market competition, and there will probably always be nodes willing to process transactions for free.
Satoshi Nakamoto
Bitcoin v0.1 release on P2P Foundation forum on Feb 11, 2009
I've developed a new open source P2P e-cash system called Bitcoin. It's completely decentralized, with no central server or trusted parties, because everything is based on crypto proof instead of trust. Give it a try, or take a look at the screenshots and design paper:
Download Bitcoin v0.1 at https://www.bitcoin.org
The root problem with conventional currency is all the trust that's required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust. Banks must be trusted to hold our money and transfer it electronically, but they lend it out in waves of credit bubbles with barely a fraction in reserve. We have to trust them with our privacy, trust them not to let identity thieves drain our accounts. Their massive overhead costs make micropayments impossible.
A generation ago, multi-user time-sharing computer systems had a similar problem. Before strong encryption, users had to rely on password protection to secure their files, placing trust in the system administrator to keep their information private. Privacy could always be overridden by the admin based on his judgment call weighing the principle of privacy against other concerns, or at the behest of his superiors. Then strong encryption became available to the masses, and trust was no longer required. Data could be secured in a way that was physically impossible for others to access, no matter for what reason, no matter how good the excuse, no matter what.
It's time we had the same thing for money. With e-currency based on cryptographic proof, without the need to trust a third party middleman, money can be secure and transactions effortless.
One of the fundamental building blocks for such a system is digital signatures. A digital coin contains the public key of its owner. To transfer it, the owner signs the coin together with the public key of the next owner. Anyone can check the signatures to verify the chain of ownership. It works well to secure ownership, but leaves one big problem unsolved: double-spending. Any owner could try to re-spend an already spent coin by signing it again to another owner. The usual solution is for a trusted company with a central database to check for double-spending, but that just gets back to the trust model. In its central position, the company can override the users, and the fees needed to support the company make micropayments impractical.
Bitcoin's solution is to use a peer-to-peer network to check for double-spending. In a nutshell, the network works like a distributed timestamp server, stamping the first transaction to spend a coin. It takes advantage of the nature of information being easy to spread but hard to stifle. For details on how it works, see the design paper at Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
The result is a distributed system with no single point of failure. Users hold the crypto keys to their own money and transact directly with each other, with the help of the P2P network to check for double-spending.
Satoshi Nakamoto
https://www.bitcoin.org
Here are 3 screenshots of the client's UI.
BitCoin v0.01 ALPHA
Copyright (c) 2009 Satoshi Nakamoto Distributed under the MIT/X11 software license, see the accompanying file license.txt or http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php. This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit (http://www.openssl.org/). This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
Intro
Bitcoin is an electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It's completely decentralized with no server or central authority.
Operating Systems
Windows NT/2000/XP (and probably Vista)
Vista hasn't been tested yet. All the libraries used are cross-platform, so there's nothing preventing future Linux and Mac builds.
Setup
Unpack the files into a directory and run bitcoin.exe.
The software automatically finds other nodes to connect to. You should set your firewall to forward port 8333 to your computer so you can receive incoming connections, otherwise the nodes you can connect with will be limited.
To support the network by running a node, select:
and keep the program open or minimized. It runs at idle priority when no other programs are using the CPU. Your computer will be solving a very difficult computational problem that is used to lock in blocks of transactions. The time to generate a block varies each time, but may take days or months, depending on the speed of your computer and the competition on the network. It's not a computation that has to start over from the beginning if you stop and restart it. A solution might be found at any given moment it's running. As a reward for supporting the network, you receive coins when you successfully generate a block.